D898_E901 RET Deletion Is Oncogenic, Responds to Selpercatinib, and Treatment Resistance Can Arise Via RET-Independent Mechanisms - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37535881/
D898_E901 RET deletion is a gain-of-function mutation and responds to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in MTC. RET Δ898-901 mutant is sensitive to selpercatinib and vandetanib, and acquired resistance to selpercatinib may...
Conclusion: D898_E901 RET deletion is a gain-of-function mutation and responds to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in MTC. RET Δ898-901 mutant is sensitive to selpercatinib and vandetanib, and acquired resistance to selpercatinib may develop via RET-independent mechanisms.
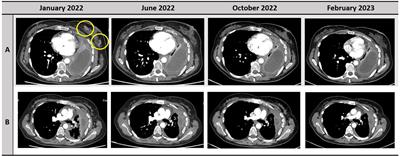
Small bowel edema and lymphocytic duodenitis as severe reversible gastrointestinal toxicity of selpercatinib in RET fusion-positive non-small cell lung cancer: a case report
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2023.1201599/full
IntroductionRearranged during transfection (RET) gene rearrangements occur in 1%-2% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Because of the results of the study LIBRETTO-001, selpercatinib has been approved as the first-line...
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first case report of a patient with NSCLC treated with selpercatinib outside a clinical study who developed severe gastrointestinal toxicity characterized by small bowel edema and lymphocytic duodenitis, leading to treatment interruption and dose reduction. The gastrointestinal AE has been described...

Clinical and Genomic Characterization of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma with Signet-Ring/Poorly Cohesive Cells - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37355152/
Signet-ring cell (SRC)/poorly cohesive cell carcinoma is an aggressive variant of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC). This study aimed to clarify its clinicopathologic and molecular profiles based on a multi-institutional cohort...
Conclusions/Relevance: Although pancreatic SRC carcinoma shares similarities with conventional PDAC regarding the most important genetic drivers, it also exhibits important differences. A personalized approach for patients with this tumor type should consider the clinical relevance of histologic determination of the SRC component and the...
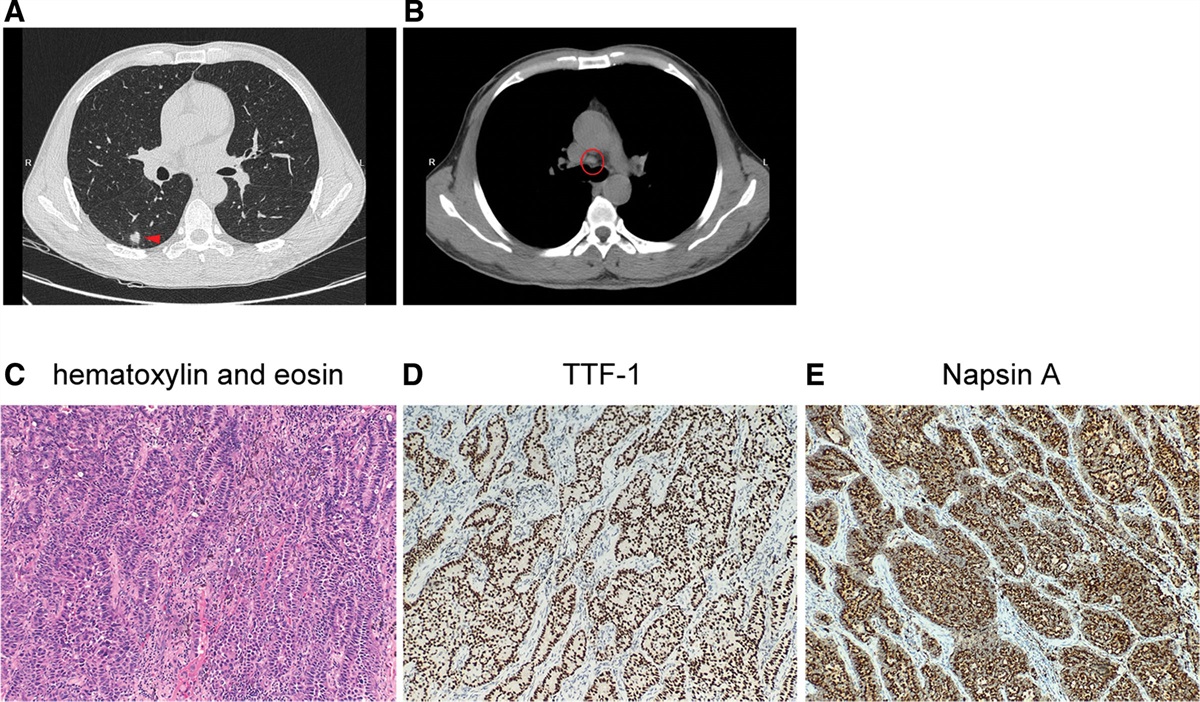
A novel PIBF1-RET gene fusion identified from a stage IA lung adenocarcinoma: A case report
pralsetinib. To date, approximately 40 fusion partners have been reported. Herein, we report a novel progesterone immunomodulatory binding factor 1 (PIBF1)-RET gene fusion identified from a stage IA lung adenocarcinoma...
Conclusion: We report a novel PIBF1-RET fusion in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma. This finding expands the spectrum of RET fusion partners and warrants further studies in characterizing the oncogenic role of this genomic aberration and response to RET-targeted therapies.

A Functional sgRNA-CRISPR screening method for generating murine RET and NTRK1 rearranged oncogenes
CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing represents a powerful tool for investigating fusion oncogenes in cancer biology. Successful experiments require that sgRNAs correctly associate with their target sequence and initiate double stranded breaks...
Conclusions/Relevance: A cell line (TR.1) established from a Trim24-Ret positive tumor exhibited high in vitro sensitivity to the RET inhibitors LOXO-292 and BLU-667 and orthotopic TR.1 cell-derived tumors underwent marked shrinkage upon LOXO-292 treatment. Thus, the method offers an efficient means to validate sgRNAs that successfully target...

