Efficacy and Safety of Pralsetinib in Chinese Advanced RET-Mutant Medullary Thyroid Cancer Patients
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38261313/
Pralsetinib has demonstrated efficacious activity in various solid tumors, including medullary thyroid cancer (MTC), as observed in the phase 1/2 global ARROW study (BLU-667-1101; NCT03037385). We evaluated the safety and...
Pralsetinib demonstrated broad, deep, and durable efficacy, as well as a manageable and acceptable safety profile in patients with advanced RET-mutant medullary thyroid cancer.

Real-World Clinical Profile, RET Mutation Testing, Treatments, and PROs for MTC in Europe
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38189657/
Patients with aMTC report substantial disease/treatment burden. Outcomes could be improved by identifying patients eligible for treatment with selective RET inhibitors through more optimal RET mutation testing.
Common physician-cited barriers to RET mutation testing included high cost, difficulty accessing latest tests, and time delay for results.
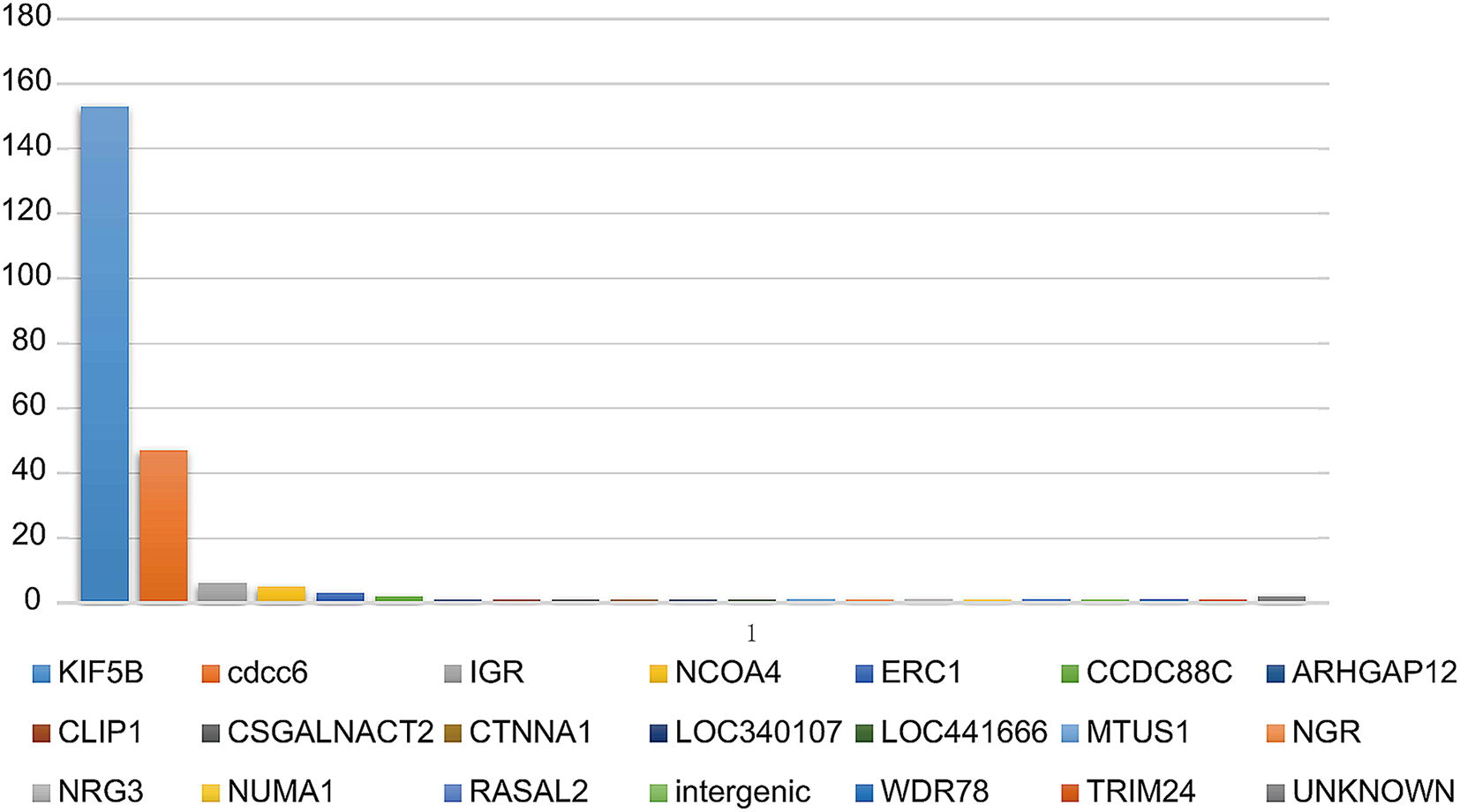
Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Combination Therapy in Metastatic RET-Mutated Lung Cancer From Real-World Retrospective Data
Source : https://bmccancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12885-024-11852-3
Background The impact of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) based treatments on non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLCs) with RET fusions remains poorly understood. Methods We screened patients with RET fusions at...
The majority of patients with RET fusion-positive mutations showed PD-L1 expression of <50% (17.8%).
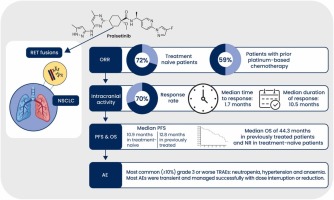
Clinical Evidence and Adverse Event Management Update of Patients With RET- Rearranged Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Treated With Pralsetinib
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1040842823003311?via=ihub
Current non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) management relies on genome-driven precision oncology thus shifting treatment paradigm towards biomarker-gu...
The introduction of pralsetinib and selpercatinib has revolutionized the landscape of RET fusion-positive advanced NSCLC by addressing most of the shortcomings and limitations of multikinase inhibitors.

Characteristics and Survival Outcomes of Patients With Metastatic RET Fusion-Positive Solid Tumors Receiving Non-RET Inhibitor Standards of Care in a Real-World Setting
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38271655/
These data suggest that RET fusions represent a negative prognostic factor in patients with metastatic solid tumors and highlight the need for wider genomic testing and use of RET-specific TKIs...
RET fusions represent a negative prognostic factor in patients with metastatic solid tumors and highlight the need for wider genomic testing and use of RET-specific tyrosine kinase inhibitors.

