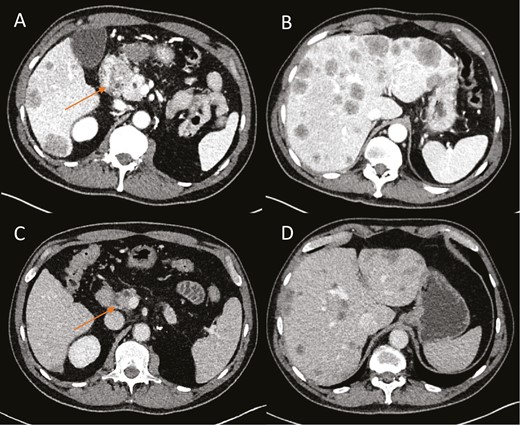
Primary Resistance to RET Inhibition in a RET Fusion-Positive Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
Source : https://academic.oup.com/oncolo/advance-article/doi/10.1093/oncolo/oyae034/7628136?login=false
This article reports a patient with pancreatic neuroendocrine carcinoma with a finding of a nuclear receptor co-activator 4-RET fusion and subsequent treatment
The patient's clinical course highlighted the fact that finding a targetable genomic alteration does not always equate to benefit for the patient.

Association of Timely Comprehensive Genomic Profiling With Precision Oncology Treatment Use and Patient Outcomes in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38452312
Timely CGP is associated with the quality of patient care as measured by 1L matched targeted therapy use, time to therapy discontinuation, and avoidance of ineffective, costly ICPIs.
Receipt of timely comprehensive genomic profiling resulted in a ≈31% decrease in use of immune checkpoint inhibitors among patients with ALK/EGFR/RET/ROS1-positive disease.

Peritoneal Effusion: an Uncommon Adverse Effects of Selective RET Inhibitors
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38369014
Peritoneal effusion: an uncommon adverse effect of selective RET inhibitors
In this letter, the authors described a rare adverse event of chylous effusion that was observed during treatment with multikinase inhibitors and selective RET tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
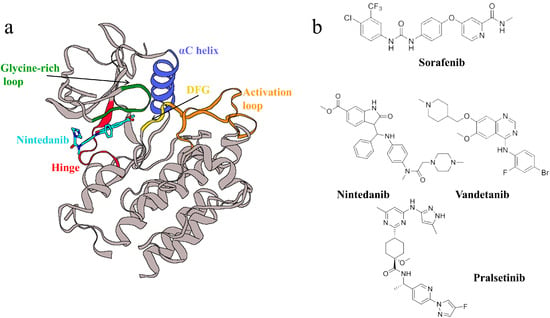
Generating Potential RET-Specific Inhibitors Using a Novel LSTM Encoder-Decoder Model
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/4/2357
The receptor tyrosine kinase RET (rearranged during transfection) plays a vital role in various cell signaling pathways and is a critical factor in the development of the nervous system. Abnormal...
The authors trained a molecular generation model based on fragment-based drug design and a long short-term memory encoder-decoder structure to generate a molecular assembly accuracy of 98.4%.

Efficacy of First-Line Treatment Options Beyond RET-TKIs in Advanced RET-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: a Multi-Center Real-World Study
Source : https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10832335/
Although RET‐tyrosine kinase inhibitors (RET‐TKIs) are the preferred first‐line therapy for advanced RET‐arranged NSCLC, most patients cannot afford them. In this population, bevacizumab, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy ...
Immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with bevacizumab and chemotherapy might be a preferred option as a first‐line therapy for RET‐rearranged NSCLC, followed by a combination of bevacizumab and chemotherapy.

