Pirtobrutinib inhibits wild-type and mutant Bruton's tyrosine kinase-mediated signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia - Blood Cancer Journal
Source : https://www.nature.com/articles/s41408-022-00675-9
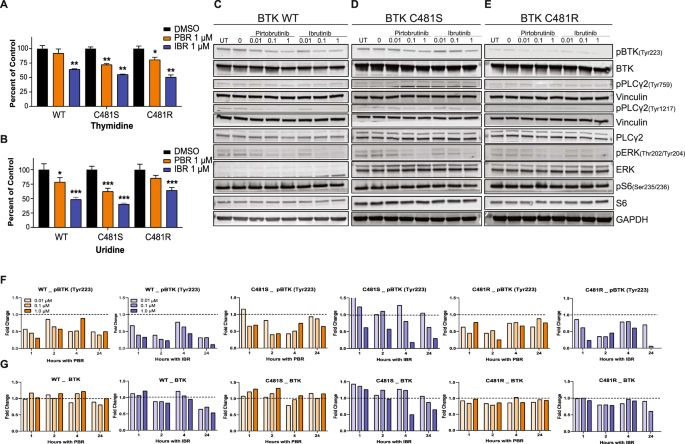
Pirtobrutinib (LOXO-305), a reversible inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK), was designed as an alternative strategy to treat ibrutinib-resistant disease that develops due to C481 kinase domain mutations. The clinical activity of pirtobrutinib has been demonstrated in CLL, but the mechanism of action has not been investigated.
Conclusion: Collectively, these results demonstrate that pirtobrutinib is an effective BTK inhibitor for CLL harboring wild-type or mutant BTK as observed by changes in CCL3 and CCL4 biomarkers and suggest that alterations in BCR pathway signaling are the mechanism for its clinical effects. Long-term evaluation is needed for BTK gatekeeper residue variation along with pathologic kinase substitution or mutations in other proteins in the BCR pathway.

• Source: Blood Cancer Journal
• Conclusion: “Pirtobrutinib appears to be an effective agent for lowering BCR-mediated signaling in cell lines as well as primary cells, including during therapy. Importantly, this drug inhibits signal transduction initiated either from wild-type BTK or kinase domain-mutant BTK. The initial inhibition of signal transduction emitting from the BCR pathway indicates successful inhibition of the BCR axis. Development of a BCR-independent clone or expansion of clones mutated in the molecules downstream of BTK needs to be evaluated along with combination strategies with pirtobrutinib.”
• In the current preclinical study, researchers used 4 different model systems or primary malignant cells to assess pirtobrutinib-mediated inhibition of the BCR signaling cascade and biological effects.
• The pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profile of Pirtobrutinib yielded initial mechanistic inhibition of the BCR pathway in CLL cells, which was demonstrated by a drop in CCL3/CCL4 biomarkers in varied BTK contexts. The indicated phase 2 dosage of pirtobrutinib is 200 mg/day.
• Once bound to the kinase, ibrutinib kills the enzyme and is thus an irreversible and covalent inhibitor compared with pirtobrutinib, which is a reversible inhibitor and does not act by irreversibly killing the BTK enzyme. Therefore, BTK levels do not decrease with pirtobrutinib, with continuous presence needed to inhibit BTK. Pirtobrutinib has a longer half life and better binding efficiency, which make it effective, per the authors.