
Cotargeting of BTK and MALT1 overcomes resistance to BTK inhibitors in mantle cell lymphoma - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36719376/
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) is a proven target in mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), an aggressive subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. However, resistance to BTK inhibitors is a major clinical challenge. We...
Conclusions: We conclude that MALT1 overexpression associates with resistance to BTK inhibitors in MCL, targeting abnormal MALT1 activity could be a promising therapeutic strategy to overcome BTK inhibitor resistance, and cotargeting of MALT1 and BTK should improve MCL treatment efficacy and durability as well as patient outcomes.
-
 Leukemia and Lymphoma Connect2yrKey Points • Source: The Journal of Clinical Investigation • Conclusions “We conclude that MALT1 overexpression associates with resistance to BTK inhibitors in MCL, targeting abnormal MALT1 activity could be a promising therapeutic strategy Show More
Leukemia and Lymphoma Connect2yrKey Points • Source: The Journal of Clinical Investigation • Conclusions “We conclude that MALT1 overexpression associates with resistance to BTK inhibitors in MCL, targeting abnormal MALT1 activity could be a promising therapeutic strategy Show More
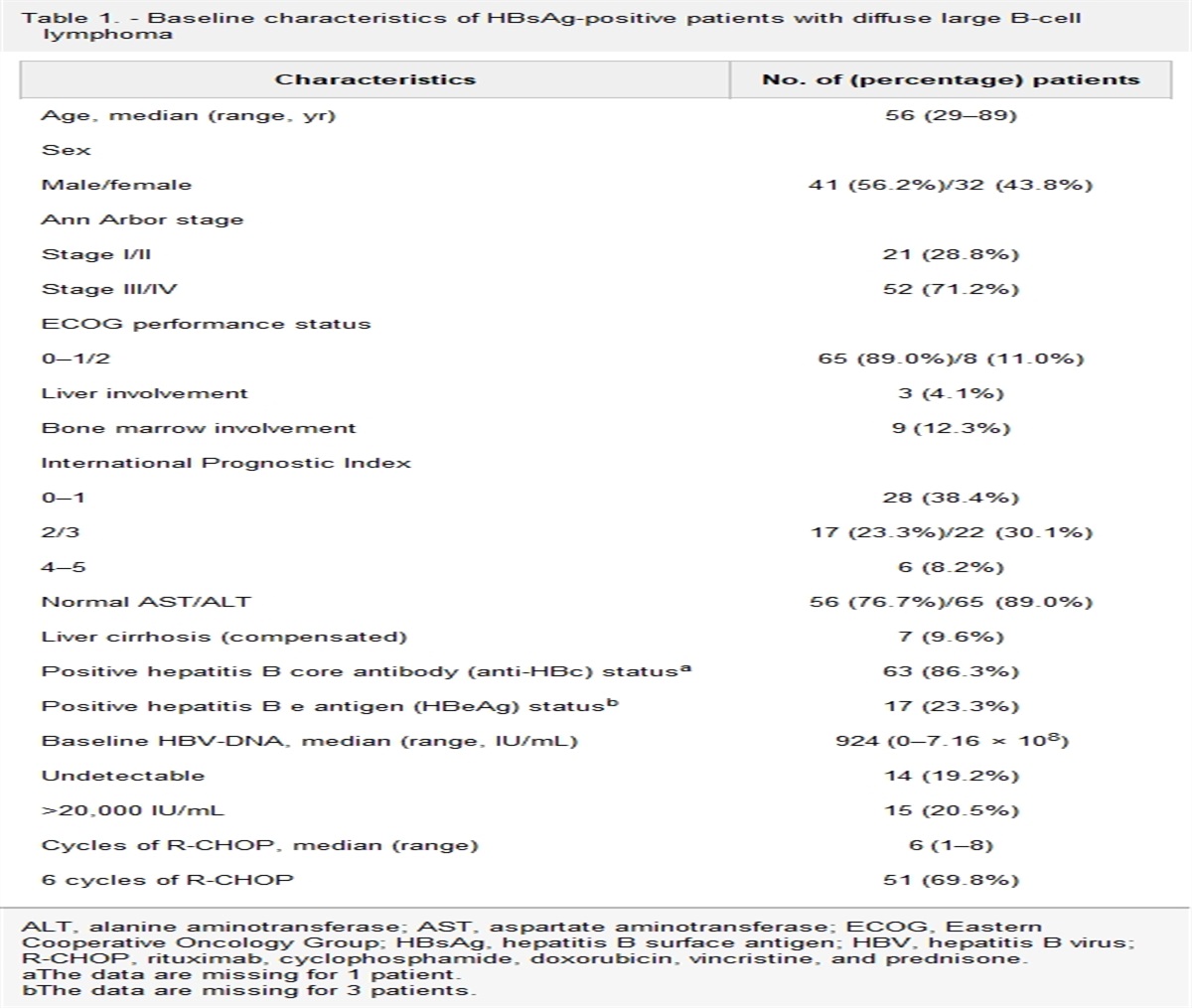
A Prospective Study of Preemptive Tenofovir Disoproxil... : Official journal of the American College of Gastroenterology | ACG
Source : https://journals.lww.com/ajg/Abstract/9900/A_prospective_study_of_preemptive_tenofovir.650.aspx
ristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) chemotherapy. METHODS: We enrolled 73 patients from 20 institutions. The primary end point was the absolute risk of hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related hepatitis during preemptive TDF...
Conclusions: Preemptive TDF therapy in HBsAg-positive patients with DLBCL receiving R-CHOP chemotherapy was safe and effective for preventing HBV-related hepatitis. However, a long-term maintenance strategy of preemptive TDF therapy should be recommended because of the relatively high rate of HBV-related hepatitis after withdrawal from TDF.

Biological therapy in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36715330/
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure....
Conclusions: Overall, this therapeutic armamentarium will constitute the basis for multimodal and personalized combinations that, in the idea of precision medicine, will enormously benefit elderly AML patients.
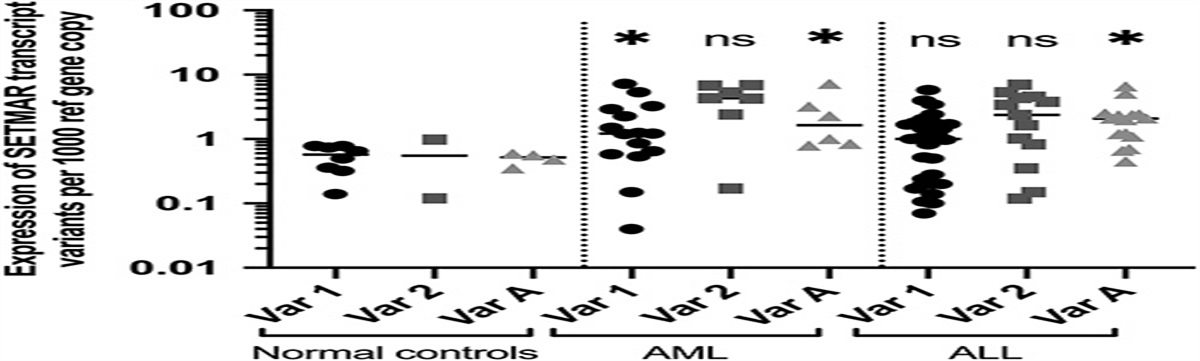
Investigating the Expression Pattern of the SETMAR Gene... : Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology
rs suggesting that it might contribute to the establishment or progression of these cancers. In leukemia, the SETMAR gene transcript variants have not been widely studied. Therefore, this study aimed...
Conclusions: According to the results, SETMAR showed increased expression in pediatric acute leukemia’s bone marrow samples, indicating a role for this molecule in leukemia pathogenesis. As this is the first report of SETMAR expression in pediatric leukemias, further studies are needed to investigate the causality of this association.

Covalent Library Screening by Targeted Mass Spectrometry for Rapid Binding Site Identification - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36706310/
Interest in covalent drug discovery has surged in recent years, following the high-profile FDA approvals of covalent inhibitors that target BTK and KRAS G12C. High-throughput screening by intact protein mass...
Conclusions: We describe the development of CoMPAS, a novel, targeted mass spectrometry-based covalent screening method that provides binding site information in the initial screen.
