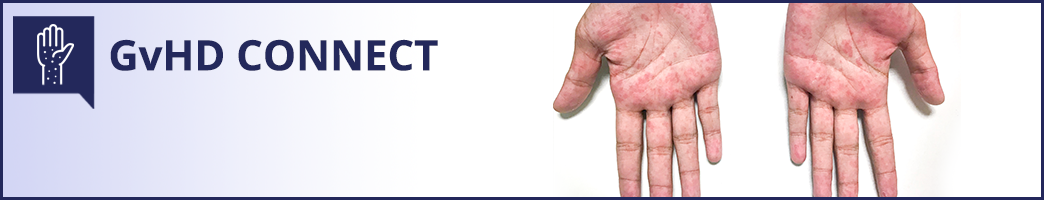
Chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD) involves multiorgan pathology, with features of both inflammation and fibrosis. The innate and adaptive immune systems likely contribute to the cause of this condition. Experts suggest that the acute inflammatory response secondary to tissue injury early posttransplant transforms to chronic inflammation and dysregulation of T and B cells. Thus, leading to impaired tissue repair and fibrotic reactions. Chronic GVHD can lead to multisystem tissue damage , with the mucosa, skin, and lung most affected. Following allogeneic HSCT, cGVHD is a leading cause of late morbidity and late non-relapsed mortality.
Although fibrosis may contribute to wound healing in some chronic inflammatory conditions, in cGVHD, it leads to chronic disability when it impacts the joints or substantial areas of skin. Fibrosis can result in life-threatening chronic respiratory deficiency when it affects the peribronchiolar pulmonary lobules. Fibrosis typically responds poorly to treatment once it is entrenched .
How do you manage fibrosis in patients with chronic GVHD following the failure of systemic therapies?
-
 Eric Schaefer2yrA MDT approach is key. Will start with supportive therapies lik PT for stiff joints. Typically I start with steroids both topical and systemic for mild to Show More
Eric Schaefer2yrA MDT approach is key. Will start with supportive therapies lik PT for stiff joints. Typically I start with steroids both topical and systemic for mild to Show More -
 ALEXANDER BARSOUK2yrSteroids and jakafi, ritux or imbruvica based on comorbidities, then Rezurock as last line resort
ALEXANDER BARSOUK2yrSteroids and jakafi, ritux or imbruvica based on comorbidities, then Rezurock as last line resort