DCZ0014, a novel compound in the therapy of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma via the B cell receptor signaling pathway
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1476558621001056?via=ihub
DCZ0014 inhibits cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. * Lyn/Syk in the B cell receptor signaling pathway are regulated in DCZ0014-induced apoptosis. * DCZ0014 inhibits tumor growth...
Conclusion/Relevance: Tumor xenograft model showed that DCZ0014 not only inhibited tumor growth but also extended the survival time of mice. Thus, DCZ0014 showed potential for clinical application in the treatment of patients with DLBCL.

Tumor cell-derived IL-10 promotes cell-autonomous growth and immune escape in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Source : https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/2162402X.2021.2003533
ABSTRACT Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive malignancy arising from germinal center or post-germinal center B-cells that retain many of the properties of normal B-cells. Here we show...
Conclusion/Relevance: In this work, we demonstrate that (1) the expression of IL-10 and IL-10R is a hallmark of DLBCL and strongly correlated with STAT3 phosphorylation and with MYD88/BCR mutations in DLBCL cell lines and DLBCL patients, that (2) IL-10 signaling is cell-intrinsically required for DLBCL growth in ectopic and orthotopic...

Prognostic implications of tumor immune microenvironment and immune checkpoint pathway in primary central nervous system diffuse large B‐cell lymphoma in the North Indian population
Source : https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/apm.13195
This article has been accepted for publication and undergone full peer review but has not been through the copyediting, typesetting, pagination and proofreading process, which may lead to differences between...
Conclusion: TME plays significant role in the prognosis of PCNS-DLBCL. Increased number of CD4 T cells and PD-L1 expressing immune cells are associated with better prognosis in PCNS-DLBCL. Further studies with larger sample size are required to evaluate the role of targeted therapy against TME and immune check point inhibitors in this disease.

Excess Mortality by Multimorbidity, Socioeconomic, and Healthcare Factors, amongst Patients Diagnosed with Diffuse Large B-Cell or Follicular Lymphoma in England - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34830964/
(1) Background: Socioeconomic inequalities of survival in patients with lymphoma persist, which may be explained by patients' comorbidities. We aimed to assess the association between comorbidities and the survival of...
Conclusion/Relevance: Deprivation is consistently associated with poorer survival among patients diagnosed with DLBCL or FL, after adjusting for co/multimorbidities. Comorbidities and multimorbidities need to be considered when planning public health interventions targeting haematological malignancies in England.
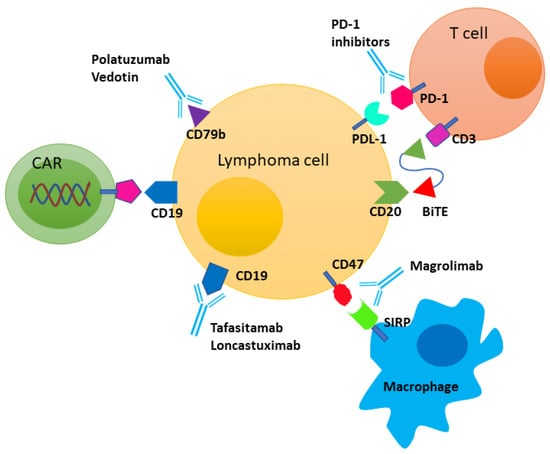
Immunotherapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Current Landscape and Future Directions
Source : https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/22/5827
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is a heterogeneous disease. B-cell receptor (BCR) pathway is essential for malignant B-cell growth, survival, and proliferation. Various immune cells, including T-cells and macrophages in...
Conclusion/Relevance: Immunotherapy has played a pivotal role in the management of relapsed DLBCL. Stem cell transplant and CAR T-cell therapy are curative treatment modalities for relapsed disease. Despite this, a subset of patients continues to progress, and their outcomes remain dismal. Newer therapeutic options to optimize outcomes as well...

