Cost-effectiveness analysis of transplant-ineligible relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treatment options-Experience of the efficiency frontier approach - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37644352/
Using the EF approach, the currently most cost-effective interventions (based on cost-effectiveness ratios) in the indication of R/R DLBCL were identified to guide international reimbursement decisions.
Conclusions: Using the EF approach, the currently most cost-effective interventions (based on cost-effectiveness ratios) in the indication of R/R DLBCL were identified to guide international reimbursement decisions.

Evolving therapeutic landscape of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: challenges and aspirations - Discover Oncology
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12672-023-00754-8
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) represents the commonest subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma and encompasses a group of diverse disease entities, each harboring unique molecular and clinico-pathological features. The understanding of...
Conclusions/Relevance: We review the recent advances in the therapeutic armamentarium of DLBCL and discuss implications on the practice landscape, with a particular emphasis on the context of the healthcare system in Singapore.

Comparative effectiveness of salvage chemotherapy regimens and chimeric antigen T-cell receptor therapies in relapsed and refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma: a network meta-analysis of clinical trials - PubMed
Source : https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37548344/
The optimal salvage chemotherapy regimen (SC) for relapsed/refractory (R/R) diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) prior to autologous stem cell transplant remains unclear. Moreover, although chimeric antigen receptor T cell (CAR-T)...
Conclusions/Relevance: Our results indicate that R-GDP may be preferred for R/R DLBCL over other SC compared. Longer follow-up is required for ongoing comparative survival analysis as data from CAR-T trials matures.

Estimating the Cost per Clinical Outcome of Second-Line liso-cel Versus ASCT in Patients With Transplant-Intended R/R LBCL
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2666636723014379?via=ihub
It is important to consider the total cost of care (TCOC) associated with a therapy and clinical benefit for relapsed or refractory (R/R) large B cell...
Conclusions/Relevance: While liso-cel–treated patients incurred greater up-front costs, fewer required subsequent therapy and accumulated less downstream costs. These results underscore the importance of considering durability of response and clinical benefit when assessing total costs.
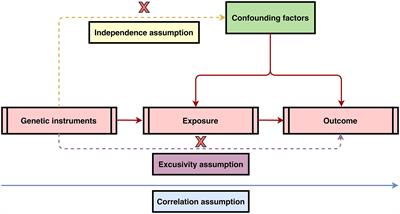
The causal effect of inflammatory bowel disease on diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1171446/full
BackgroundIt has been reported that inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is associated with an increased risk of malignancies, including lymphoma. A number of large observational studies have been devoted to exploring...
Conclusions: The above MR study concluded that IBD itself is causally responsible for DLBCL, especially Crohn’s disease. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the mechanism underlying this direct causal link.

