Endothelial activation and stress index as a prognostic factor of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: the report from the nationwide multi-center Thai Lymphoma Study Group - Annals of Hematology
Source : https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00277-023-05437-6
Several prognostic models have been introduced to predict outcomes of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). Endothelial activation and stress index (EASIX) is a surrogate of endothelial dysfunction which...
Conclusion: EASIX score was significantly associated with survival outcomes and may be used as a simple prognostic tool to better risk-classify DLBCL.

A novel NET-related gene signature for predicting DLBCL prognosis - Journal of Translational Medicine
Source : https://translational-medicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12967-023-04494-9
Background Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) is an aggressive malignancy. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) are pathogen-trapping structures in the tumor microenvironment that affect DLBCL progression. However, the predictive function of...
Conclusions: We developed a genetic risk model based on NRGs to predict the prognosis of patients with DLBCL, which may assist in the selection of treatment drugs for these patients.
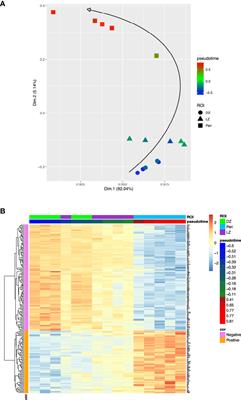
Pseudotemporal ordering of spatial lymphoid tissue microenvironment profiles trails Unclassified DLBCL at the periphery of the follicle
Source : https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2023.1207959/full
We have established a pseudotemporal ordering for the transcriptional signatures of distinct microregions within reactive lymphoid tissues, namely germinal center dark zones (DZ), germinal center light zones (LZ), and peri-follicular...
Conclusions/Relevance: This report offers a thought-provoking perspective on the relationship between transcriptional profiling of functional lymphoid tissue microenvironments and the evolving concept of the cell of origin in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas.
Lisocabtagene maraleucel for second-line relapsed or refractory large B-cell lymphoma: patient-reported outcomes from the PILOT study
Source : https://haematologica.org/article/view/haematol.2023.283162
In the single-arm, open-label, multicenter, phase 2 PILOT study, second-line treatment with the chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with relapsed or refractory (R/R) large...
Conclusions/Relevance: In within-patient analyses, clinically meaningful improvements or maintenance in scores were observed in most patients at days 90, 180, 270, and 365. HRQOL was maintained or improved in patients who received liso-cel as second-line therapy in PILOT. These findings support liso-cel as a preferred second-line treatment in...
Model for predicting central nervous system relapse in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and discussion of prophylaxis measures
Source : https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1878875023012123?via=ihub
Relapse of the central nervous system (CNS) is a rare but fatal complication in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). The purpose of this study is to...
Conclusion: CNS relapse is associated with high risk CNS-IPI and testicular involvement. Therefore, it is necessary to pursue novel prophylactic strategies for CNS relapse.

